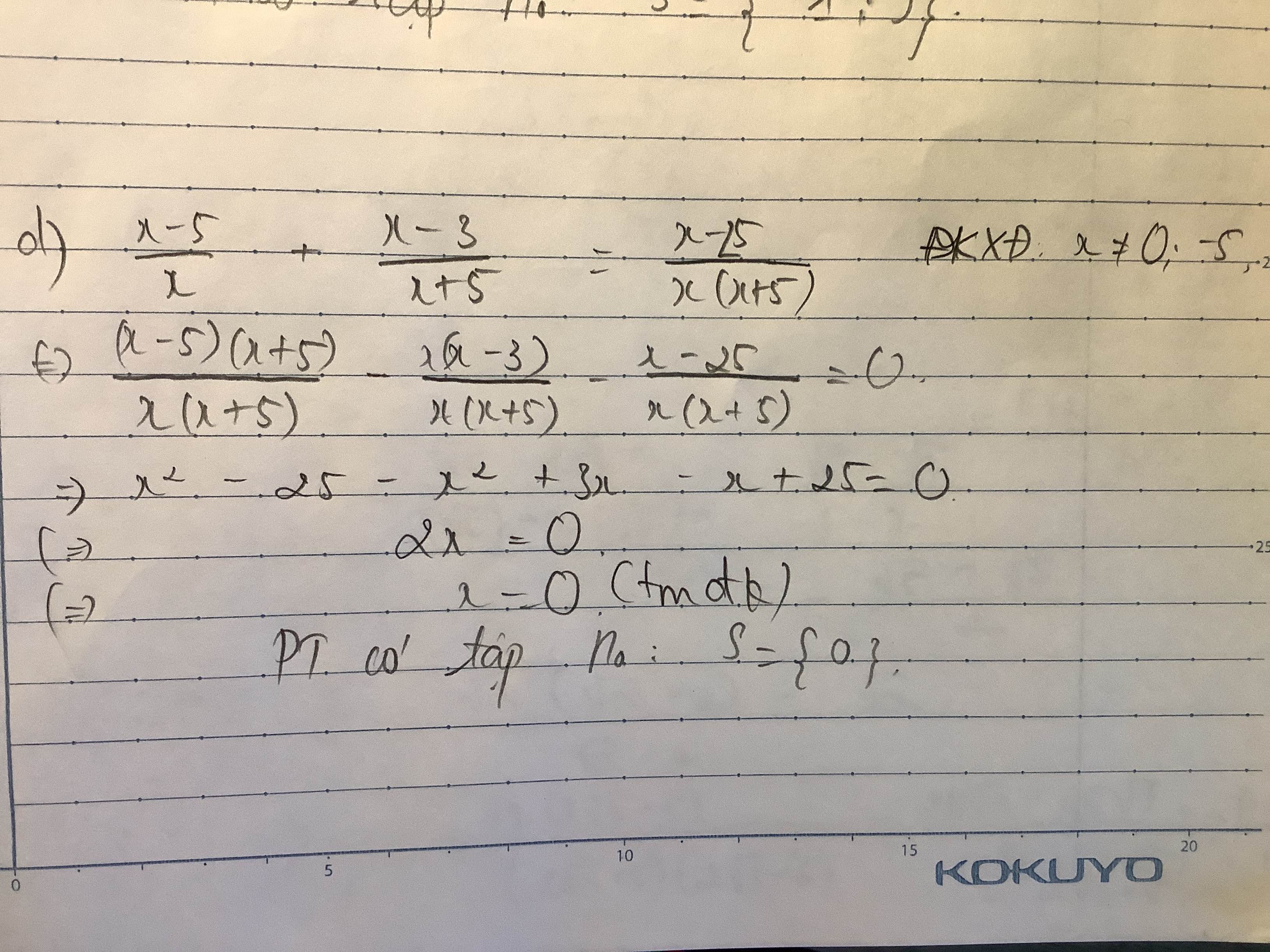[Lớp 8]Bài 1. Giải phương trình sau đây:a) 7x+121;b) left(4x-10right)left(24+5xright)0;c) left|x-2right|2x-3;d) dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-dfrac{1}{x}dfrac{2}{xleft(x-2right)}. Bài 2. Giải bất phương trình sau đây và biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên trục số: dfrac{x-1}{3}-dfrac{3x+5}{2}ge1-dfrac{4x+5}{6}. Bài 3. Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của A-x^2+2x+9. Bài 4. Giải bài toán bằng cách lập phương trình:Một người đi xe máy dự định đi từ A đến B với vận tốc 36km/h. Nhưng khi thực hiện ngư...
Đọc tiếp

[Lớp 8]
Bài 1. Giải phương trình sau đây:
a) \(7x+1=21;\)
b) \(\left(4x-10\right)\left(24+5x\right)=0;\)
c) \(\left|x-2\right|=2x-3;\)
d) \(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{2}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\)
Bài 2. Giải bất phương trình sau đây và biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên trục số:
\(\dfrac{x-1}{3}-\dfrac{3x+5}{2}\ge1-\dfrac{4x+5}{6}.\)
Bài 3. Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của \(A=-x^2+2x+9.\)
Bài 4. Giải bài toán bằng cách lập phương trình:
Một người đi xe máy dự định đi từ A đến B với vận tốc 36km/h. Nhưng khi thực hiện người đó giảm vận tốc 6km/h nên đã đến B chậm hơn dự định là 24 phút.
Tính quãng đường AB.
Bài 5. Cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao. Vẽ HD⊥ AB (D ∈ AB), HE ⊥ AC (E∈ AC). AB=12cm, AC=16cm.
a) Chứng minh: ΔHAC đồng dạng với ΔABC;
b) Chứng minh AH2=AD.AB;
c) Chứng minh AD.AB=AE.AC;
d) Tính \(\dfrac{S_{ADE}}{S_{ABC}}.\)